Taxonomy Mapping Concepts
The Enterprise CoreDb database taxonomy levels (OrgUnitLevel) do not have the same taxonomy as the EOM entities. However, both the Enterprise CoreDb database and the EOM database provide the same enterprise organizational structure. To ensure that both match, the EOM entity taxonomy levels must be mapped to the Enterprise CoreDb database taxonomy levels using the EOM Synchronization file.
Understanding Taxonomy
The retailer’s enterprise organizational structure follows a taxonomy, which is the classification of the different entities that belong to the organization. Taxonomy data is stored in two separate databases:
- CoreDb—used by the Enterprise Solutions applications.
- RTEEnterpriseOptionsData—used by Enterprise Options Management (EOM).
Enterprise Solutions taxonomy
The Enterprise Solution applications maintain the following taxonomy data:
- The taxonomy that is used by various applications in the OrgUnit table of the CoreDb database. This data contains the hierarchical data for the retailer.
- The taxonomy levels in the OrgUnitLevel table in the CoreDb database. This data is used to organize the structure of the taxonomy data.Note
The OrgUnitLevel data can be configured for each retailer.
- The master data. To ensure that all applications are synchronized, all taxonomy maintenance should be done to the master data.
The following table lists sample data for the enterprise solution’s organizational units, stored in the CoreDb database.
| CoreDb org level unit ID | CoreDb org level name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Corporate |
| 2 | Enterprise |
| 3 | Region |
| 4 | Country |
| 5 | AdministrativeArea |
| 6 | Store |
These values will be available in your system only if Sample Data was selected during installation.
Enterprise Options Management (EOM) taxonomy
The EOM software maintains its own taxonomy, which the application uses to display the organizational hierarchy on various software screens. EOM also uses this taxonomy for sending data to the correct stores. This data is stored in the Entity table of the RTEEnterpriseOptionsData database, and is similar to the data located in the OrgUnit table of the CoreDb database, which is used for the other enterprise applications. The following image displays a sample organizational hierarchy in the EOM application. The EOM user interface displays the Name field from the Entity Table.
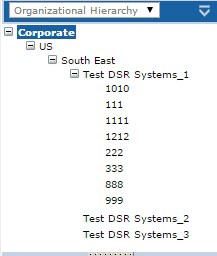
Each organizational level in EOM corresponds to an entity type, which identifies it in the system. Entity types are used to organize the structure of the taxonomy data. Entity types are stored in the Name field of the EntityType table. The org levels displayed in the preceding image of the EOM software correspond to the following entity types in the RTEEnterpriseOptionsData database.
| EOM org level name | EOM entity type name |
|---|---|
| Corporate | Brand |
| US | Country |
| South East | Region |
| Test DSR Systems_1 | State |
| 1010, 111, and so on | DSR Server |
The EOM organizational level names can be changed by the retailer. The entity types are fixed within the EOM taxonomy and cannot be changed.
Troubleshooting EOM Synchronization
If a retailer uses the EOM Synchronization Service, Ncr.Retail.Services.EOMSynchronization, this service automatically transfers taxonomy changes made in CoreDb to EOM’s RTEEnterpriseOptionsData database. The following tools are available to help troubleshoot the EOM Synchronization service:
- The log file, EOMSynchronization.txt, is located in the %ProgramData%\NCR\RetailOne\Enterprise\LogFiles folder.
- Logging by Log4Net is configurable in the EOM Synchronization configuration file.
Retailers may choose not to use the EOM Synchronization service, but instead keep both databases synchronized manually using batch files.